This graph gives you an insight that how much work a team completes in a Sprint. Sprint Velocity is calculated on the rate of User Stories completion in a Sprint. It is dependent on team’s estimate of User Stories and actual work delivered per Sprint.
- The Average Velocity can help you deduce the rate at which User Stories are being completed by the team.
- This, in effect, lets you conclude that how efficiently the team is estimating or operating if it is found to be lacking on either side, corrective measures can be taken to address the difference.
- Changes in new Sprint Velocity and average velocity will reflect whether an improvement has been made.
- Estimate better for your future plans by looking at this graph. If your team capacity and Sprint duration remain same, you can have a hunch of how much effort your team can handle in next Sprints.
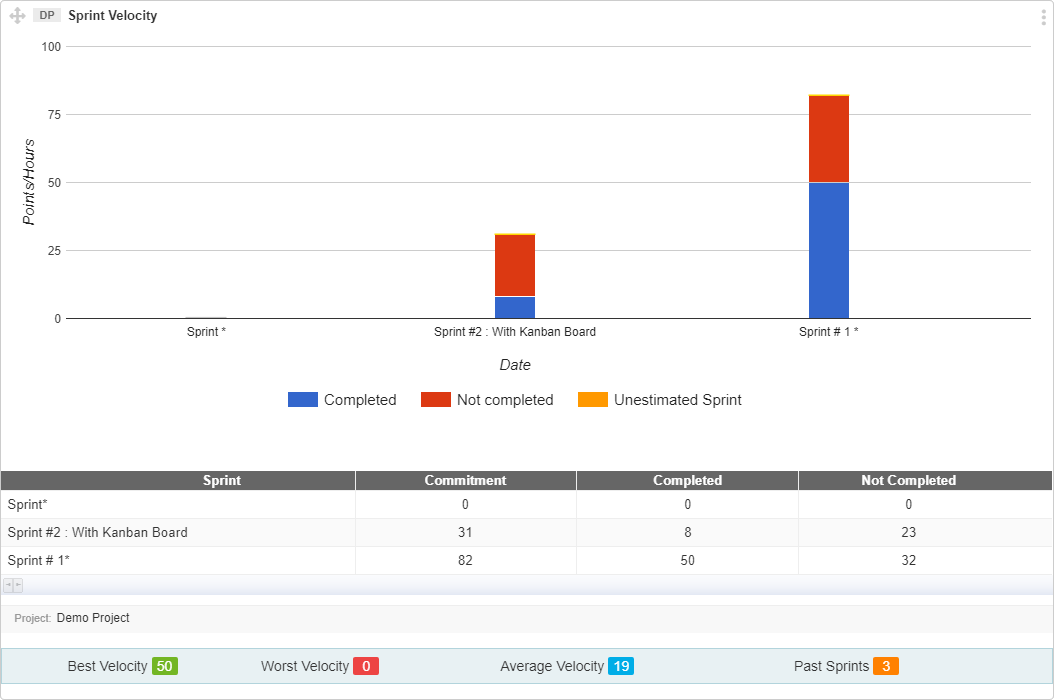
How to Interpret this graph
- The Y-axis of the graph shows you Plan Estimates. It can be Points or Hours, depending on your project settings.
- The X-axis of the graph shows you Sprints.
- Best velocity is the maximum velocity of your team among selected Sprints.
- Worst velocity is the minimum amount of completed User Stories points in a Sprint.
- Average Velocity is calculated by sum of selected sprint velocity/number of sprints
- Past Sprint reflects the number of Sprints counted while calculating the best, worst and average velocity. You can choose between 3, 5 or 10 Sprints while creating the graph.
- Sprint Velocity graph collects information of one selected project. You can also include Active Sprints in the graph.
- If you enable the “Show Table” option while creating a graph, a stats table will appear below the graph.
Track progress better
To better track progress with the Sprint Velocity graph, make sure if you are performing these:
- Define your Sprint duration and keep it same throughout the project.
- Specify and update each User Story estimation in Planning sessions.
- Use Effort Log feature for Tasks and Issues to estimate better in next Sprints
- Encourage the team to be realistic while estimating User Stories. Be aware that estimate still can not reflect the actual time.
- For better planning, estimate User Stories relative to other items in backlog. If you know from earlier Sprint, that one somewhat similar user story took x days then use it as a reference for estimating the new user story.
- Break a large User Story into multiple User Stories. It is proven that humans estimate better for the small countable amount of work.
Sprint Velocity at Sprint Board
In addition to Dashboard, you can also view your Sprint velocity through Sprint board.
